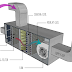
Air conditioning system on ships
What are the objectives of air conditioning on ships?
- To extract excess heat
- To raise air temperature when required
- To add moisture as required
- To reduce moisture content as required
- To maintain sufficient oxygen and airflow
- To remove dust
How control of temperature is attained?
- The comfortable temperature range is about 22 °C and relative humidity (RH) about 60% (usually 40 ~ 70%)
All zone temperature
- Controlled by compressor suction pressure, via solenoid valve as step controlling.
- Thermostat, placed at some accommodation space actuates the Master Solenoid Valve of the plant, which will stop the Compressor when the preset temperature is reached
- Capacity unloader of compressor units does last step controlling, as required
Particular zone temperature
- Controlled by a flap valve fitted in each zone loop
- The local cabin temperature can be adjusted by volume control at the delivery point of the air duct controller.
Write a note on Ozone depletion?
- Ozone is gas; between 15 & 30 kilometers above the surface of the earth.
- This layer controls our climate & protects us from radiation.
- The release of industrial waste and other processes are now increasing the ozone breakdown to disturb the natural balance.
- Pollutant (e.g. CFC) gas from ground level travel to the atmosphere.
- In the upper atmosphere, Ultra Violet Ray breaks off Chlorine atom from the CFC molecule.
- The free chlorine atom attack the one ozone molecule. Breaking it form to chloro monoxide. The remainder of the ozone molecule is formed into a regular oxygen molecule.
- A free oxygen atom now steels the oxygen from the chloro monoxide molecule form an oxygen molecule. The chlorine atom is again free, attack and break up an ozone molecule. In this way, a single chlorine atom destroys 1 million of ozone molecules.
Ozone depletion leads to:
- More ultraviolet radiation
- Global warming
- Increasing skin cancer
- Immune system affected
- Reduced forest production and crops
- Sea ecology disturbed.
- More greenhouse gas
- Warmer & more humid climate
- More desert
- Less forest
- Higher sea level
- Sea ecology system destroy
Refrigerant affected to Ozone layer: R11 (CClF ), R12 (CCl2F2), R22 ( CHClF2)
Refrigerant not affected to Ozone layer: NH3, R134A
What are the leakage tests for various refrigerants?
CO2 – Soap and water solution
NH3 – Wet litmus paper ( Red to Green ); Sulphur candles, which give off white dense smokes when contact with ammonia.
Freon – Soap and water solution / Halide torch /Electronic leak detector (buzzer sound)
How to indicate the flame by halide torch?
- Content is methylated spirits type.
- Butane can also be used.
- When the leak is detected the flame will change from blue to green depending on the concentration of gas.
What is refrigeration?
- It is a process in which the temperature of a space or its contents is reduced to below that of their surrounding.
What is the air conditioning?
- It is the control of temperature and humidity in a space together with the circulation, filtering, and refreshing of the air.
What is the ventilation?
- It is the circulation and refreshing of the air in the space without necessarily a change of temperature.
What is a comfort zone?
- It is between the 40 to 70 % relative humidity at the temperature of 20 to 29 °C dry bulb temperature and air motion is 100mm per sec.
What are the advantages of secondary refrigerant?
- Low initial cost
- Low maintenance cost
- Suitable for large refrigeration plant
- Easily produced on board by mixing CaCl2 and distilled water.
- Easily store as salt on board
What is defrosting?
- A method of removal of frost, built-up on evaporator coils. Defrosting should be done before snow thickness exceeds ¼”.
What are the reasons for defrosting?
- Affecting heat transfer properties
- Affecting air flow and circulation
- Liquid back to the compressor
What are the defrosting methods?
- By stopping the system
- By washing with warm water
- Using electric heater coil fitted at the evaporator
- By hot gas defrosting method
How to defrost the brine system?
Hot brine thawing
- The best and fastest method used a powerful brine heater with a separate thawing system. Watertight trays under the pipes, collect the dripping water.
Hot air from the atmosphere
- Isolating doors in air trunks must be perfectly tight, to prevent hot air from going into cargo spaces.
By shutting off the brine
- Allow the snows to be melted by the heat of the air in circulation. Very slow operation and tends to throwback a great deal of moisture into cargo space.
What is the purpose of ventilation for cargo hold?
- To remove surplus heat and humidity
- To prevent the condensing of moisture on cargo or hull
- To remove gases produced in the ripening process of some fruits and vegetable cargos.
What is short cycling?
- It is a condition of a compressor unit repeatedly running for a few seconds and then cutting out. This is the result of the L.P controller.
Why high pressure cut out is fitted?
- It is fitted to shut down the compressor in the event of high pressure. After remedying the fault, it must reset manually.
Why fitted the master solenoid valve for a large plant?
- If the compressor stops due to a fault, the master solenoid valve will close to prevent flooding by liquid refrigerant and possible compressor damage.
Explain about one method of refrigerant charging?
Normally charging is made through the liquid charging valve at the high-pressure side.
- Firstly, weighting the gas bottle.
- Connect the gas bottle and charging valve with the connection pipe.
- Before tightening the cap on the charging pipe, open the bottle valve to remove the air in the pipe.
- Then tighten the cap and open the bottle valve fully, the charging valve is still closed.
- Change the compressor to manual running and start it.
- Close the condenser outlet valve.
- Pumping down the entire charge to the condenser.
- Open the charging valve slowly when suction pressure just above zero.
- Control the valve opening slowly that no frost formed on the compressor suction pipe.
- Check the level in the condenser sight glass.
- Close the charging valve and pumping down the entire charge until suction pressure just above zero.
- Stop the compressor and close the discharge valve.
- The cooling water kept running for some hour.
- Then the air is purged out through the purging valve on the condenser until the refrigerant gas appears at the valve.
- Calculate the amount of refrigerant (charging) and enter the engine logbook.
Why superheat is required at the evaporator outlet?
- To prevent the liquid refrigerant from entering into the compressor.
- If no superheat, hammering may happen and the valve will suffer damage and breakage.
How to fill fridge plant compressor oil?
- Change the compressor to manual running.
- Pumping down the entire charge to the condenser.
- Connect the L.O hand pump to L. O filling valve after air is purged out.
- When compressor suction pressure just above zero, open the oil filling valve, inject the L.O into the crankcase.
- Then stop the compressor and close the compressor discharge valve. Then cool down the refrigerant.
- Then purged out the air through the purging valve until the refrigerant appears at the purging valve.
What are the types of expansion valves?
- Thermostatic control
- Electronic control
- Manual control
How to prevent liquid flow back to the compressor?
- Liquid shock valve (on cylinder head)
- Thermostatic Expansion Valve
- Master solenoid valve (when the plant is at standstill, especially in Large plant)
- Defrosting
- Bursting disc (on the cylinder head, between inlet and discharge manifold)
Why back pressure valve is fitted?
- It is fitted at the outlet of the vegetable room to prevent undercooling of cargo.








No comments